Background
Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL) is an aggressive and most globally prevalent subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with a dismal prognosis. Selinexor (ATG-010) is an oral selective inhibitor of nuclear export, which blocks exportin1 (XPO1). The US FDA granted accelerated approval to selinexor for the treatment of adult patients (pts) with DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least 2 lines of systemic therapy based on the Phase 2b SADAL study (NCT02227251). SEARCH is a single arm, Phase 2, registrational bridging study to assess efficacy and safety of selinexor in Chinese pts with R/R DLBCL.
Method
SEARCH was designed to evaluate safety and efficacy of selinexor (60mg Days 1 and 3 of Weeks 1 to 4 of each 4-week cycle) in R/R DLBCL pts in China with 2-5 prior lines of systemic therapy. The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC). The study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03992339), with the primary analysis results presented here.
Results
As of 31 st May 2023 (6 months post last pt dosed), 5 (8.3%) of the 60 treated pts remained on treatment. Median follow-up was 27.7 months (mo) (range: 6.0-37.7).
Median age was 58.5 years (20.0%≥70yrs). Median duration from initial DLBCL diagnosis was 1.8 years (range: 0.5-11.2). A total of 7 pts (11.7%) had DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma, 4 (6.7%) had creatinine clearance <60ml/min and 27 (45.0%)/33 (55.0%) had GCB/non-GCB subtype, respectively. Median number of prior regimens was 3 (range: 2-5); 5 pts (8.3%) had received prior ASCT. Patients had received the following novel treatments, which were not previously received by patients in SADAL: 10 (16.7%) chidamide, 8 (13.3%) BTK inhibitor, 6 (10.0%) PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, 3 (5.0%) polatuzumab, 1 (1.7%) PI3K inhibitor, and 4 pts (6.7%) had undergone CAR-T cell therapy. Thirty-two pts (53.3%) were with primary refractory DLBCL and 54 pts (90.0%) were refractory to the last systemic therapy for DLBCL.
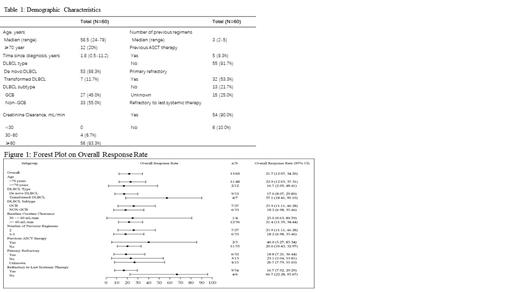
ORR was 21.7% (95% CI: 12.1, 34.2) and CR rate was 16.7%. Median duration of response (DOR) was 7.6 mo, median progression free survival (PFS) was 1.9 mo, and median overall survival (OS) was 8.5 mo.
Efficacy was evident in pts who had poor prognostic factors, including elderly pts (≥70yrs) with ORR 16.7%, pts with renal dysfunction with ORR 25.0%, primary refractory pts with ORR 18.8% and pts refractory to their last systemic therapy with ORR 16.7%. And pts with De novo/transformed DLBCL with ORR 17.0%/57.1%, pts with GCB/non-GCB DLBCL with ORR 25.9%/18.2%, pts with/without prior ASCT with ORR 40.0%/20.0%, pts with 2/more than 2 previous regimens with ORR 25.9%/18.2%. One pt (1/4) with prior CAR-T achieved PR assessed by investigators.
All pts experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE), 47 (78.3%) with at least one Grade 3/4 TEAE, and 24 (40.0%) with at least one serious TEAE. The most common non-hematologic TEAE of any grade (≥20%) included decreased appetite (61.7%), nausea (58.3%), weight loss (38.3%), vomiting (33.3%), diarrhea (31.7%), asthenia (30.0%), hyponatremia (26.7%), constipation (25.0%) and AST increased (20.0%). The most common grade≥3 non-hematologic TEAE (≥2%) were decreased appetite (6.7%), diarrhea (5.0%), vomiting (5.0%), hyponatremia (3.3%), asthenia (3.3%), pneumonia (3.3%), dyspnea (3.3%) and COVID-19 pneumonia (3.3%). The most common hematologic TEAE of any grade (≥20%) were thrombocytopenia (83.3%), leukopenia (81.7%), neutropenia (80.0%), anemia (75.0%) and lymphopenia (30.0%). The most common grade≥3 hematologic TEAE (≥10%) were thrombocytopenia (41.7%), leukopenia (40.0%), neutropenia (36.7%), anemia (23.3%) and lymphopenia (16.7%). The most common AEs were generally manageable by dose modification and supportive care.
Conclusions
R/R DLBCL remains a high unmet medical need, especially in pts who are ineligible/frail to transplantation. The SEARCH study demonstrates clinically meaningful ORR in Chinese R/R DLBCL pts treated with selinexor monotherapy, consistent with the global study. Adverse events were generally manageable with appropriate supportive care and dose modification. These data are generally consistent with the SADAL study and supports the use of selinexor as an oral, chemotherapy-free treatment option for R/R DLBCL patients in China.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal